Although cryptocurrency is no longer a foreign mythical concept like it used to be 5 years ago, it is still misunderstood by a lot of people. All the hype surrounding digital assets and projects like NFTs, DeFi, metaverse, and Web 3.0 has contributed to “cryptocurrency” and “blockchain technology” becoming trendy words often heard in tech news and even mainstream media. However, many people still view crypto as nothing more than a speculative tool.
As a crypto user myself, I often have to answer the “What is cryptocurrency?” question asked by my friends and relatives. In a face-to-face conversation, I usually just say, “It is like money, but one that isn’t attached to a bank or any government — it is fully anonymous and belongs only to its users.” However, there is also a longer, more comprehensive answer. In this article, I will do my best to demystify the concept of cryptocurrency and show how useful it can actually be. Let’s go!
How Does Cryptocurrency Work? Crypto Explained
The idea of an electronic form of money was in the air a long time ago. However, it was only implemented in 2008, when someone published the Bitcoin white paper.
In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto (an anonymous individual or, perhaps, a group of people hiding behind this pseudonym) completed the development of the Bitcoin program code, the first cryptocurrency. Back then, the first block was generated, and the first 50 bitcoins were mined. This is how the world learned about blockchain technology, which is now applied far beyond digital money. Today, we have a lot of different popular cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum, Solana, Toncoin, and many others.

Cryptocurrency is a program code. It does not have an offline version, and each coin is protected from fraud by a hash. All digital money exists only in the network space.
Unlike traditional currency, cryptocurrencies are decentralized. There is no central bank or a group of users that could change the current rules without the consent of the parties. Instead, there is a peer-to-peer network of computers (nodes) wherein each participant runs software that connects them with others to exchange information.
In a banking system, users have to interact with each other through a central server. A decentralized cryptocurrency system has no hierarchy: nodes connect and transmit information to each other.
The decentralization of cryptocurrency networks makes them highly resistant to shutdown and censorship. In contrast, in order to disrupt the centralized network, you just need to interrupt the main server. If the bank erases its database and has no backups, it will be challenging to determine user balances.
In cryptocurrency, all nodes keep copies of the database (or the blockchain, a digital ledger where all transactions are stored). Each node effectively functions as its own server. If some nodes go offline, others can still receive information from the remaining ones.
Thus, cryptocurrencies operate 24 hours a day and 365 days a year. They allow the transfer of value anywhere in the world without the intervention of intermediaries. This is why we often call them free from restrictions: anyone with an Internet connection can transfer funds.
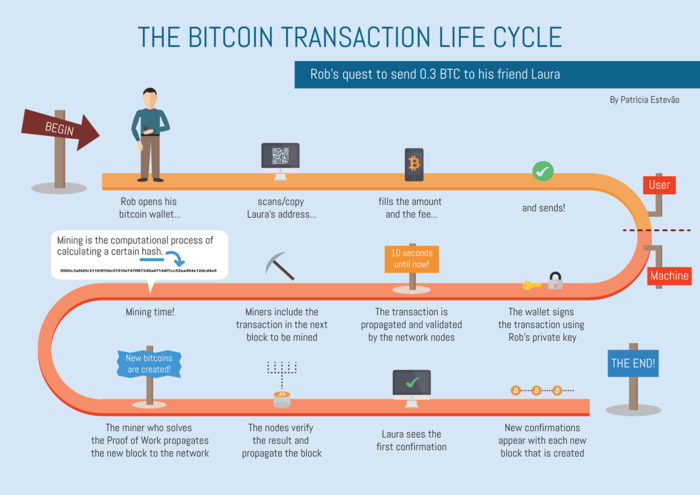
Let’s look at the example. Here we have two people with mobile wallets. Alice wants to transfer 1 Bitcoin to Bob.
- Alice creates a transaction that transfers 1 BTC to Bob’s wallet. A transaction includes the sum, the recipient’s Bitcoin address, and a digital signature created with Alice’s private key.
- Nodes check whether Alice really has 1 Bitcoin and the transaction is legit (contains the digital signature).
- Every node updates the blockchain version and adds the info about Alice’s transaction. The blockchain keeps the info about all transactions.
- Alice and Bob use software — a wallet — to interact within the network. It can manage keys and incoming and outgoing transactions and also send/receive cryptocurrency. When the transaction is checked, Bob gets the notification about the received money, as well as Alice — about the completed transaction.
Types of Cryptocurrency
There are many other virtual currencies besides Bitcoin. These coins are called ‘altcoins’ — or alternative coins — and there are thousands of them on the market. The most well-known are Ethereum, Litecoin, Polkadot, etc.
The coins that are pegged to any fiat currency or gold are called stablecoins. One of the stablecoins with a large market capitalization is Tether (USDT); its price is pegged to the US dollar. USD Coin (USDC) is another popular stablecoin. STASIS EURO (EURS) is pegged to the euro, and BiLira (TRYB) to the Turkish lira. PAX Gold is a stablecoin backed by one fine troy ounce (t oz) of a 400 oz London Good Delivery gold bar stored in Brink’s gold vaults.
One more type of cryptocurrency is a token. A token is a unit other than a cryptocurrency: it’s designed to represent a digital balance in a certain asset. We’ll explain the difference between coin and token later.
There are also NFTs — non-fungible tokens. Technically, there are not exactly cryptocurrencies, but rather digital representations of an asset, be it physical or not, recorded on the public ledger, blockchain. An NFT can be anything from a piece of art to a real-life building or a tweet.
How to Use Cryptocurrency? Crypto Use Cases
Cryptocurrencies are in great demand due to their decentralized nature. Besides, the wide acceptance pool outside the crypto community makes cryptocurrency useful in many ways. Let’s take a look at some of its use cases.
Digital Payments
Cryptocurrencies are great for making day-to-day transactions, although volatility is still an important factor explaining why most merchants do not accept them as a payment method. However, as time goes by, more and more merchants are starting to support digital currency.
Cryptocurrency transactions are much easier now than they used to be a few years ago. New technologies, such as layer 2, or the transformation of the Ethereum blockchain from the proof-of-work consensus mechanism to the proof-of-stake one, have provided both merchants and regular users with cheap and efficient ways to transfer digital assets.
Transactions
In addition to being used as a payment method, crypto assets can find their application in transferring money cheaply and efficiently. Unlike traditional fiat currencies, Bitcoin and altcoins aren’t restricted by local laws and regulations, providing a cheaper and faster alternative to traditional transaction methods like bank transfers, especially for remittances sent to countries with less developed banking systems.
Trading
Cryptocurrency has also opened up numerous opportunities for beginners and advanced traders to diversify their trading options. While stocks, forex, and commodities trading are common things to an investor, crypto trading helps expand your investment portfolio.
Apart from regular crypto and crypto-fiat pairs, cryptocurrency investors can now also make use of more complex trading features such as futures, margin trading, and more — all of these are slowly but surely being introduced on an increasing number of platforms.
Learn more about Bitcoin ETFs here.
Anti-Corruption and Anti-Poverty Tool
Cryptocurrencies allow approximately 40% of people around the world to identify themselves in the financial world if you count people without a bank account and living in developing countries. However, in some countries, such as Myanmar, this number reaches as much as 95%. There are some reasons for this event such as the bank’s remote location, the lack of sufficient assets, and the lack of necessary documentation.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain can provide people with access to financial services. This is important for accumulating savings, obtaining loans, paying for goods and services on the Internet, and investing, which they could not do before cryptocurrencies. All of these, in turn, can contribute to poverty reduction.
Moreover, bank employees can track, freeze, decline, or seize the payments. The authorities of some countries are already resorting to this practice. Do you remember what happened to WikiLeaks in 2010? The US government pressured Visa and Mastercard to freeze all the WikiLeaks donations made through traditional payment channels.
Cryptocurrencies can help to fight inflation. In 2008, the Zimbabwean dollar rate collapsed by 1023%. It was a 100% average daily inflation rate. The same situations occurred in Yugoslavia in 1994, Peru in 1990, Ukraine in 1994, and Hungary in 2017. The use of cryptocurrencies does not imply such market situations.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
This is a recent and fast-growing application. DeFi platforms use smart contracts on blockchain networks, primarily Ethereum, to recreate traditional financial systems like loans, interest accounts, and exchanges without intermediaries.
Read this article to learn more about DeFi.
Privacy and Censorship Resistance
Some cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash offer enhanced privacy features, making transactions completely untraceable. This can be crucial for individuals in regions with strict financial censorship or those who prioritize financial privacy.
Store of Value
Bitcoin, in particular, is often referred to as “digital gold” due to its limited supply and decentralized nature, with some seeing it as a hedge against inflation and a store of value similar to precious metals.
Tokenization of Assets
Cryptocurrencies can represent other forms of value. For instance, tokens can be issued to represent shares in a company, real estate, or any other form of real-world asset, making asset ownership and transfer more fluid.
Supply Chain and Authenticity Tracking
Cryptocurrencies and the underlying blockchain technology can be used to create transparent and immutable records for supply chains, ensuring product authenticity.
Fundraising and Crowdsales
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), Security Token Offerings (STOs), and other token-based fundraising methods have emerged as alternatives to traditional investment models.
Gaming and Virtual Goods
The gaming industry has seen integration with cryptocurrencies for buying in-game items, land, or characters. Some games even have their economies based on cryptocurrencies.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Cryptocurrencies
Here are some of the advantages cryptocurrencies can provide.
- Since it is impossible to freeze the account or withdraw the cryptocurrency, coins are available on your account at any time. You can check the reliability of the operations performed.
- Unlike fiat or electronic money, transactions with which are easily tracked, it’s quite complicated to get information about the owner of a cryptocurrency wallet. Only the wallet number and limited data on the account balance are available. This makes cryptocurrency anonymous.
- As a rule, cryptocurrency is issued in a limited volume, which draws the attention of investors and eliminates the risks of inflation due to the excessive activity of the issuer. Thus, cryptocurrency is not subject to inflation and is inherently a deflationary currency.
- Cryptocurrency is a synonym for decentralization. Nobody regulates its issue and does not control the movement of funds on the account. Mostly, this feature attracts many members of the network.
- There is no commission for transferring funds between countries. Users pay the fees required by the blockchain to complete the transaction.
- All you need to start using crypto is a digital wallet — no need to provide your personal information or issue any debit/credit cards.
And here are some of the disadvantages of cryptocurrency.
- Government structures do not have trust in cryptocurrency. Governments of quite a few countries do not look at cryptocurrencies as a real asset. Moreover, digital coins are prohibited in several jurisdictions.
- Refunds are incredibly hard to perform, and transactions are irreversible due to the immutable nature of blockchain technology.
- Volatility. Cryptocurrency price is unpredictable, as it depends on the current demand. Consequently, there are fluctuations in the price of virtual money.
- The private key to electronic money is a special password. If you lose it, the crypto coins in your wallet become unattainable.
- Each user is personally responsible for their savings. There are no regulatory mechanisms here, so it will not be possible to prove anything and return the money in case of theft.
Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
Cryptocurrencies are mostly legal worldwide. However, there are some exceptions. We’ve created a table on the governments’ relation to the Bitcoin statement. Please note that some countries are not included.
| Illegal | Legal | Undefined* |
| Algeria | Nigeria | Namibia |
| Egypt | Mauritius | Canada |
| Morocco | Angola | Columbia |
| Bolivia | South Africa | Russia |
| Afganistan | The USA | Saudi Arabia |
| Nepal | El Salvador | Jordan |
| China | Mexico | Taiwan |
| Bangladesh | Costa Rica | Cambodia |
| Nicaragua | Vietnam | |
| Jamaica | Tanzania | |
| Argentina | Zimbabwe | |
| Brazil | Ecuador | |
| Chile | UAE | |
| Venezuela | Turkey | |
| Uzbekistan | Thailand | |
| Kyrgyzstan | ||
| Cyprus | ||
| Israel | ||
| Lebanon | ||
| India | ||
| Hong Kong | ||
| Japan | ||
| South Korea | ||
| Malaysia | ||
| Philippines | ||
| Singapore | ||
| Brunei | ||
| The UK | ||
| Central African Republic | ||
| Australia |
*Undefined mostly means that cryptocurrencies are not recommended for use by the government but are not prohibited. Please check the rules and regulations in your country before buying or trading any cryptocurrencies.
Coin vs. Token
At first glance, coins and tokens appear to be the same. Both are traded on cryptocurrency exchanges and can be moved between blockchain addresses. However, there’s a big difference between them.
A coin is a digital asset that is a full-fledged cryptocurrency. You can understand that it is a coin in front of you by various technical characteristics. But don’t be alarmed — we will not go into details and “poke around” in the code. It is better to consider two main features by which you can easily and quickly distinguish coins from tokens:
- All coins have their own blockchain.
- Coins are full-fledged and multifunctional “digital money.”
A token is an internal conditional unit in the blockchain of a particular cryptocurrency. Intended to perform a specific function, tokens cannot be considered full-fledged independent cryptocurrencies. Unlike coins, tokens do not have the features that we listed above:
- Tokens do not have their own blockchain.
- A token is not digital money.
Read more about the differences between token and coin in our article.
Should You Invest In Cryptocurrencies?
If you are all set to start your investment experience, Changelly is happy to offer you the best cryptocurrency purchase rates. But before, we would like to give you some investment advice:
- DYOR! Study the market carefully before buying any cryptocurrency. There are always risks, and sometimes very big ones.
- Do not think that if Bitcoin cost $20,000 last night and $19,999 this morning, you should immediately buy it. It’s not a stock market. You need to monitor the quotes and wait for the right moment closely.
- It cannot be assumed that the cryptocurrency is growing at any moment and you are guaranteed to make money on it. As we said in the example above, we must keep in mind that the market value is always several percent higher than the purchase price.
- Do not rush to invest. A good deal doesn’t happen as often as you’d like. Analyze the market and be patient.
Now you are all set! If you are already excited about cryptocurrencies and want to start your investment experience, we are here to help you.
Here are some of the best cryptocurrencies you can buy now.
FAQ
How long do cryptocurrency transactions take?
Cryptocurrency transactions are essentially a transfer of digital currencies from one party to another. The time it takes for these transactions to be completed can vary widely based on several factors. For instance, the congestion in the cryptocurrency market and the transaction fee you’re willing to pay can impact speed. It also depends on the crypto asset’s consensus mechanism — proof of work, proof of stake, and so on.
To illustrate, let’s take a look at PoW. Once a transaction is made, it gets verified through a process called cryptocurrency mining. Miners verify transactions and then add them to a blockchain. Some crypto transactions, like those with Bitcoin, might take 10 minutes to an hour or even longer, while others with different digital currencies can be almost instantaneous.
It’s essential to note that while the transaction itself might be fast, some financial institutions and crypto exchanges might have additional processing times before you can access or use your own cryptocurrency.
Is Bitcoin a digital currency?
Yes, Bitcoin is a digital currency. It was, in fact, the very first cryptocurrency introduced to the world. Unlike national currencies issued by governments and financial institutions, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network using blockchain technology. This technology helps record transactions securely and transparently, making Bitcoin and other digital currencies unique in the way they handle financial transactions.
What is the difference between centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges?
Centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges are platforms where people can buy, sell, or trade digital currencies. The main difference lies in how they operate.
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) are run by companies or organizations, much like traditional financial institutions. They act as intermediaries, facilitating trades and often holding user funds. Examples include Coinbase and Binance.
On the other hand, decentralized exchanges (often abbreviated as DEXs) operate without a central authority. They use smart contracts to facilitate crypto transactions directly between users. This means you always own cryptocurrency directly, without the need to trust a third party. While DEXs offer more privacy and control, they might be less user-friendly than CEXs.
You can learn more about the differences between CEX vs. DEX here.
Is blockchain technology only used for cryptocurrency?
No, blockchain technology is not exclusive to the cryptocurrency realm. While it underpins digital currencies and ensures the security and transparency of cryptocurrency transactions, its potential applications stretch far beyond that.
Blockchain can be used to record transactions of any type, not just financial ones. Various industries, from supply chain management to healthcare, are exploring ways to incorporate blockchain to improve transparency, traceability, and efficiency. The technology offers a way to create immutable, timestamped records without the need for centralized oversight, making it attractive for a multitude of applications.
Are NFTs cryptocurrency?
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are not cryptocurrencies in the traditional sense. While both NFTs and cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology to verify and record transactions, they serve different purposes.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum are designed to act as mediums of exchange, store value, or units of account. NFTs, on the other hand, represent unique digital assets or proofs of authenticity and ownership. You can think of them as digital collectibles or certificates of authenticity for digital items. While you can have thousands of identical Bitcoins or Ethereums, each NFT is distinct, and that’s what gives them value in the eyes of collectors or enthusiasts.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.
#Cryptocurrency #Crypto #Explained